Primary Colors: colors that cannot be created from other colors and from which all other colors can be mixed.
Red, Yellow, Blue
Secondary Colors: a primary color mixed with an adjacent color yields a secondary color.
Orange, Green, Purple
Teritiary Colors: A secondary color mixed with the adjacent primary yields a teritiary.
Red purple, Red orange, Yellow Orange, yellow green, Blue Green, Blue Purple
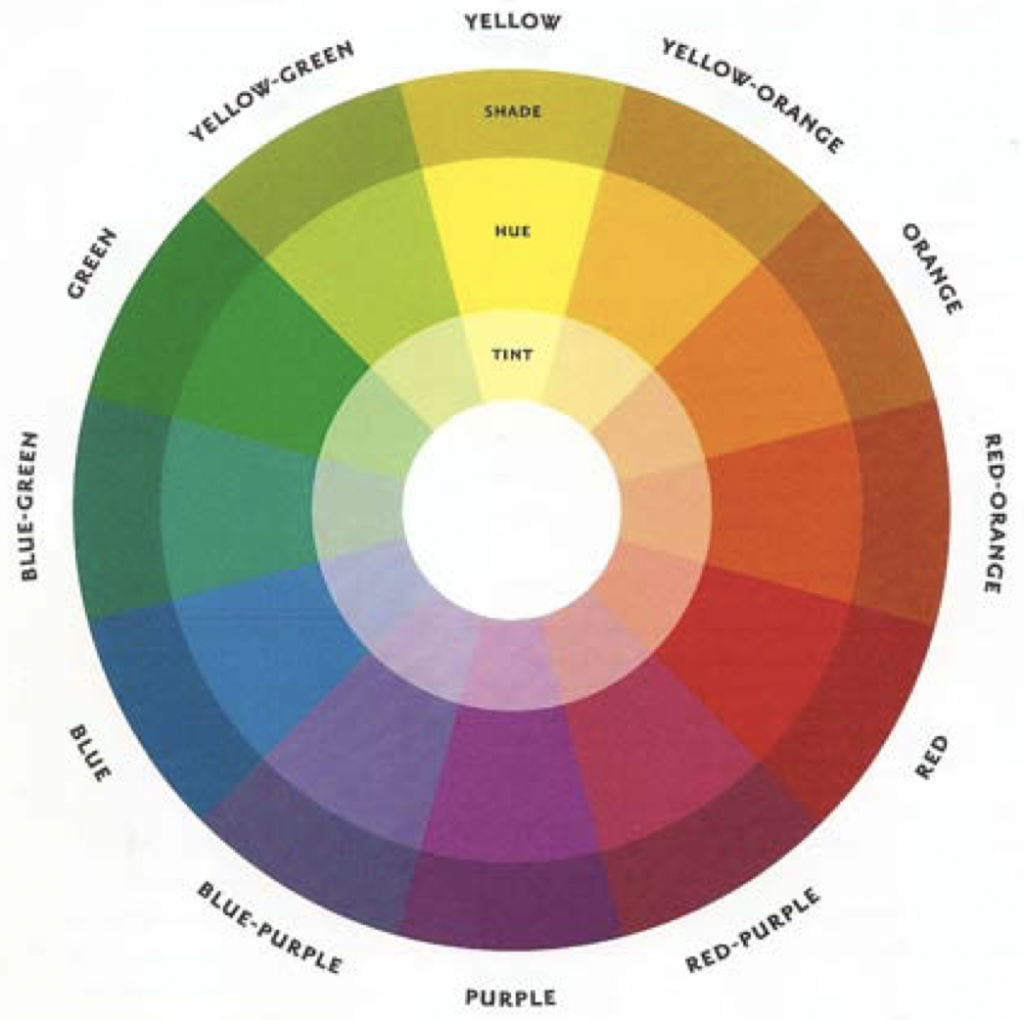
Properties of Color
Hue / Color family – The name of a color, such as red, blue, yellow, green, orange. One of the three attributes of color, which distinguishes red from green, blue from yellow, and so forth.
Value – The lightness or darkness of a color; pure colors will vary greatly in value. An attribute of color used in the Munsell System to indicate the lightness of an object viewed in daylight, on a scale from 0 for the ideal black to 10 for the ideal white, in steps that are visually equal.
Saturation / Chroma – The measure of brilliance, intensity or purity of a color. Attribute of color used in the Munsell color system to indicate the degree of departure from a gray of the same value. Correlates with the dimension of saturation.
Temperature – The warmth or coolness of a color; also relative terms in comparison to other colors in context. The temperature of a color within its hue, either warm (towards red) or cool (towards blue). Red is warm and blue is cool, but there are warm blues (those with green) and cool red (those with violet). Yellow with orange is warm and with green is cool.
Complementary Colors are two hues directly opposite each other on the color wheel. Complement to a primary color is the combination of other two primaries. Complement to Red is Green (Y+B), to Yellow is Purple (R+B), to Blue is Orange (R+Y). Complementary colors GRAY each other when mixed together. When placed side by side complementary colors intensify each other.
Neutral Hues are the results of combining all three primaries in various amounts, thus neutralizing the intensity and saturation of a hue. Combining a primary with its complement results in a neutral hue.
Split Complements – color combination whereby a hue is used with hues lying to either side of its direct complementary.
Analogous – Hues that lie next to each other on the color chart.
Shades- these are pure hues or tones mixed with black to lower its value not changing the tone.
Tint-A pure hue or tone mixed with white to change its value not its tone.
Tones- Various grays made by mixing compliments. A hue is toned down by mixing its optical opposite to cancel intensity of pure color.
Glaze- small amount of paint mixed with a medium which allows light to pass through the creating a transparent paint film.
Impasto- A thickly painted surface.
A la prima- A painting made in one session.
Figure/ground- Negative/Positive space in a picture plane.
Monochromatic- Referring to a color combination based on variations in value and saturation of a single hue.
Rods- Light-sensitive cells in the eye that operate in dim light to distinguish values.
Cones -Special cells in the retina at the back of the eye which enable us to distinguish hues in daylight.
Receeding properties: COOLNESS, GRAYNESS, DARKNESS (LOW VALUE)
Advancing properties: WARMTH, INTENSITY, PURITY, SATURATION, LIGHTNESS (HIGH VUE).
For more information, please visit the Munsell Color Standards.
Watch my Color Play video at Versal.com
Color Lab #1
Color Wheel Assignment Steps:
- Draw a circle
- Divide the circle in half horizontally
- Draw a “V” shape from the center to the outside edge.
- Draw a “V” shape to mirror the first.
- Label the hue family on the outside edge
- Place your colors around the color wheel on the outside edge.
- Mix each hue with white on the outer edge to find the tint. A pure hue mixed with white.
- Mix across the color wheel to create complimentary neutrals.
- You should wind up with 3 rings of color.
- Tint on the outer edge (mix white with a small amount of color)
- Pure spectral hue in the middle (pure paint out of the tubes)
- Neutralized values in the middle (mixing 2 colors across the color wheel)
- 3 primary colors yield 3 secondary and 6 tertiary colors totaling 12 colors.
Color Lab #2
Black Color Studies
Chromatic black vs. Ivory/Mars/ Carbon black boosted with color
Chromatic Black Recipes:
Phaltho Green + Quinacridone Red =
Pthalocyanine green + alizarin =
Ultramarine blue + an earth color (burnt sienna, burnt umber, raw sienna, or raw umber)
Prussian blue + alizarin + earth =
Alizarin + ultramarine = violet black
Red + yellow + blue =
Ivory black + hue = specific temperature black
Color Lab 1 & 2 Due Date: 2nd week of class